Where Data Tells the Story
© Voronoi 2026. All rights reserved.
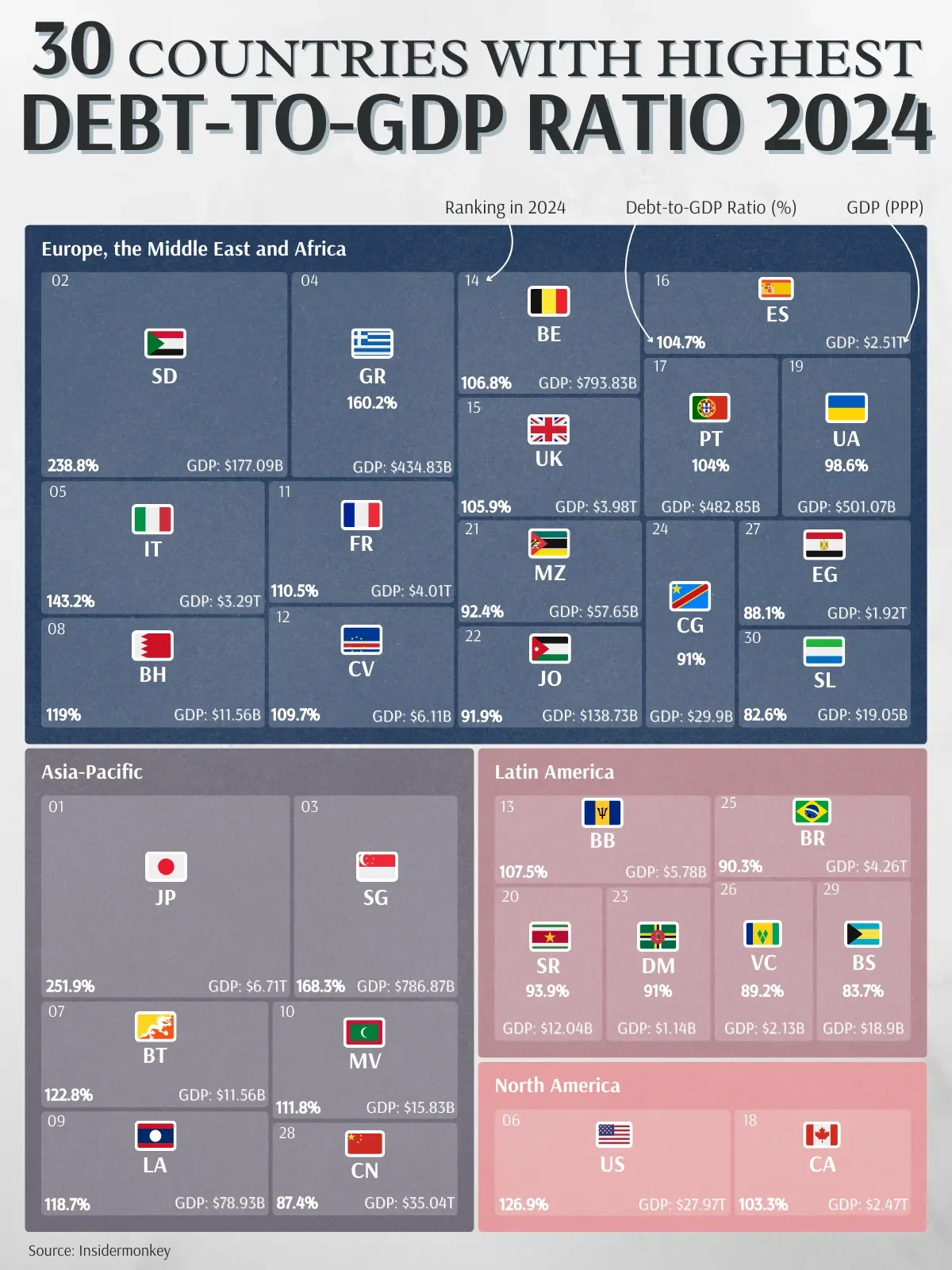
Global Debt-to-GDP
According to the IMF Global Debt Database, the global public debt fell from 10% of GDP in 2022 for the second consecutive year to 238% of GDP. In fact, global public debt has tripled since the mid-1970s, reaching 92% of GDP or $91 trillion by the end of 2022. Private debt also saw a similar increase, tripling to 146% of GDP, or $144 trillion, from 1960 to 2022.
Major Players with Higher Debt
China has played a significant role in the recent surge of global debt, alongside the United States. Currently, China’s total debt stands at around $47.5 trillion, which is less than the US's near $70 trillion. Notably, China holds the largest share of non-financial corporate debt globally, at 28%. Both China and the U.S. are among the countries with the highest debt-to-GDP ratios.
In the Asia-Pacific region, Japan leads the pack with the highest debt-to-GDP ratio at an astonishing 251.9%. This is largely due to decades of economic policies and an aging population. Singapore follows, with a debt-to-GDP ratio of 168.3%, driven by its strategic investments and financial policies. Bhutan, a small country, also has a high ratio at 122.8%, reflecting its efforts to finance development projects.
Middle East region has a mix of countries with high debt levels. Sudan is at the forefront with a debt-to-GDP ratio of 238.8%, reflecting its economic struggles and reliance on borrowing.
The data also show that many emerging and low-income economies are facing high risks of debt distress. For instance, 25% of emerging economies are at risk of default-like spreads on their sovereign debt, while about 15% of low-income economies are already in debt distress, with another 45% at high risk.